
While the ability to predict the future has always enticed mankind, its accuracy has been an aspect of debate. Data science is addressing this issue and is instrumental in accurately predicting future events associated with equipment and its performance.
The Industrial Revolution 4.0 is powered by unprecedented technological advancements with cutting-edge technology and analytical solutions delivering massive value across industries. The key advancements that mark this era are Big Data, the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Data Analytics and technology-enabled remote services that automate and drive business operations with intelligent actionable insights.
While economies across the world continue to recover from the disruption caused by the COVID-19 pandemic over the past two years, it has significantly affected the retail sector. We see reduced foot traffic in retail stores, thereby compelling leadership teams to adopt and accelerate digital transformation of store operations. As part of this digital transformation, data and the resulting intelligence tend to be the solution for addressing the business needs of hour, i.e., operational excellence, improved customer experience and sustainable growth.
What is Predictive Maintenance?
Predictive maintenance is a data-driven analytical approach to estimate when preventive maintenance needs to be performed on in-service equipment for it to work continuously and efficiently. This approach aims at reducing unnecessary or delayed maintenance of equipment. This can reduce costs and the possibility of downtime due to equipment failure compared to the traditional, schedule-based preventive maintenance approach.
Operations and maintenance data, along with equipment data derived from connected IoT devices, is collected, processed, and analyzed on an Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) platform. Such platforms are typically powered by intelligent ML algorithms to forecast device failures based on equipment health and usage patterns. This helps in planning preventive maintenance based on the actual condition of the equipment and addressing issues before they occur.
Predictive Maintenance for Retailers
The retail industry continues to stay dynamic and operate on an ever-transforming set of operational guidelines that are increasingly data-driven and evolving to keep up with consumer expectations. As digital and physical purchasing channels blend into one, to set themselves apart, retailers must consistently innovate to bring customers back to their stores.
One such innovation is the application of AI in retail operation through Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems in smart commercial buildings.
For a sector like retail, where equipment dependency is high for operations, investing in digital maintenance can yield multiple benefits including equipment reliability, equipment uptime and maintenance cost savings.
According to a report published by McKinsey, there is a potential for some companies to improve equipment availability by 5-15% and reduce maintenance costs by 18-25% by adopting fully digitized predictive maintenance.
“The average company can reduce its spend on preventive maintenance by up to 50%” as noted in a market study by ARC Advisory Group. Another report by the same firm finds that “only 18% of assets have an age related failure pattern, while a full 82% of asset failures occur randomly. This means 82% of assets are not actually in jeopardy of failure due to age, and the preventive maintenance performed on assets is ineffective.”
This is where predictive and condition-based maintenance become instrumental in making maintenance more effective.
Anticipated Benefits of Predictive Maintenance in Retail
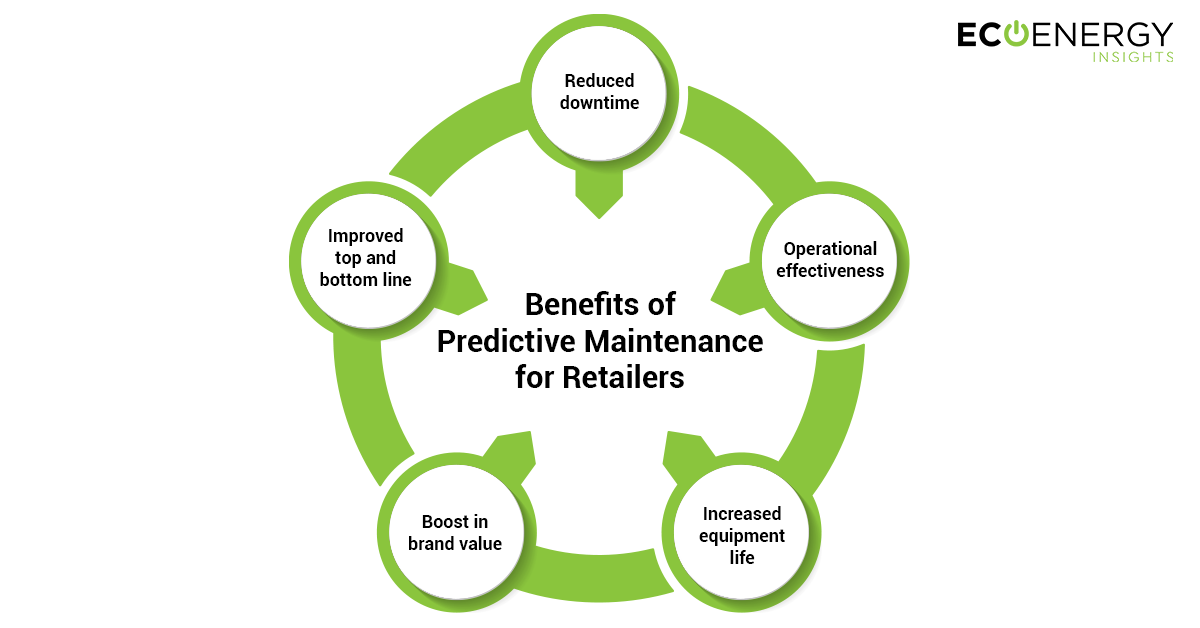
- Reduced downtime: Unplanned downtime is one of the major concerns of operations and one of the largest contributors to maintenance cost. It is not just the instance of equipment downtime, but also the duration for which the equipment was non-functional. Predictive maintenance forecasts the possible failure well ahead of time to plan for necessary spares and repairs, thereby avoiding unplanned downtime and often significantly reducing the duration that equipment is out of commission.
- Operational effectiveness: Over time, predictive maintenance helps improve operational efficiency by optimizing utilization of maintenance resources and maintenance spend. This also helps in better utilizing the resource pool for any unavoidable reactive maintenance, which almost always requires urgent human intervention. Digitizing planned maintenance enables remote fixes and makes maintenance more efficient.
- Increased equipment life: With the ability to forecast failures accurately and limit avoidable breakdowns, even aged equipment may become more reliable, thus increasing return on investment. The mean time between failures (MTBF) is an example of a key metric that can be used to indicate improvement.
- Boost in brand value: With effective maintenance of equipment health and reduced downtime, store equipment can run optimally longer . This could lead to an improved customer and employee in-store experience as well as avoidance of food spoilage or losses (in certain cases), thereby improving brand image.
- Improved top and bottom line: While initial implementation costs for predictive maintenance might be comparatively higher than the traditional preventive maintenance cost, it comes with an attractive expected return on investment and potential savings for retailers in maintenance cost avoidance annually. With the ambience in the store maintained as per set policies, customer comfort and eventually sales are likely to improve over time.
How do Retailers Adopt Predictive Maintenance?
Adopting predictive maintenance involves changing current operations and requires advanced technical skills and expertise in diverse equipment and control systems, along with the capability to analyze data and derive meaningful and precise predictions.
The prerequisite for a predictive maintenance approach is data, both operational data and data that is directly sourced from the equipment through IoT devices. Along with this, an intelligent AIoT platform is required to process this data into actionable insights. As a best practice, it is recommended to outsource this to a recognized service provider or a PaaS (Platform as a Service) provider, with a proven capability of delivering maintenance management as a service in the retail sector. This reduces the time, effort and most importantly the cost of developing the platform independently. With the right support and coordination, the maintenance service provider must be able to set up the infrastructure to provide the maintenance management service with a predictive approach through its AI platform and deliver it as proposed.
Challenges and how to mitigate them:
- Finding the right platform or service provider
- The right service provider must have proven experience delivering outcomes in maintenance management, driven by its AI platform. The retailer can further minimize risk with an outcome linked pricing model to ascertain the savings and reliability of the service. Alternately, instead of the maintenance service as a package, if only a platform is required, the retailer should look for an industry leading AIoT platform, recognized in the space of AI and IoT, that can provide actionable insights that are easy to comprehend and implement.
- Initial setup cost
- Depending on the service provider and the pricing model, a suitable business case should be established to minimize the initial cost.
- Legacy equipment
- Connectivity through IoT devices is possible even for legacy equipment, provided the service provider has suitable technical expertise and is up to speed with the latest and most reliable technologies in the IoT space.
- Integration issues
- One of the key concerns that retailers have is inbound access - both User to System and System to System. For System to System solutions, advanced options are available, where data transfer can be enabled through a ‘data push-out’ from the retailer's network to the cloud IoT platform over a secure https channel instead of the IoT platform having to pull data out. This is a real benefit to such solutions. For User-to-System access, both Site-to-Site (S-S) and Client-to-Site (C-S) VPN based models with 2 or 3 factor authentications provide additional security levels.
- Upskilling maintenance staff
- In the case of a multi-site enterprise customer, managing and training numerous maintenance staff across multiple locations can be a challenge. This can be addressed by the maintenance service provider offering remote support to the on-field maintenance staff, before and during the maintenance, thus minimizing the requirement of extensive training and monitoring. In addition, the platform should be capable of delivering reports, with recommendations as a prioritized action list, to further simplify execution for maintenance staff.
Carrier Abound CORTIX™ Platform for Retailers
The digitization of maintenance in the retail sector is now becoming more mainstream, and in today’s age, is an important requirement in running store operations. At EcoEnergy Insights, we have the technology, such as the CORTIX™ AI and IoT platform, and the expertise to enable retailers to launch and scale up the use of predictive maintenance.
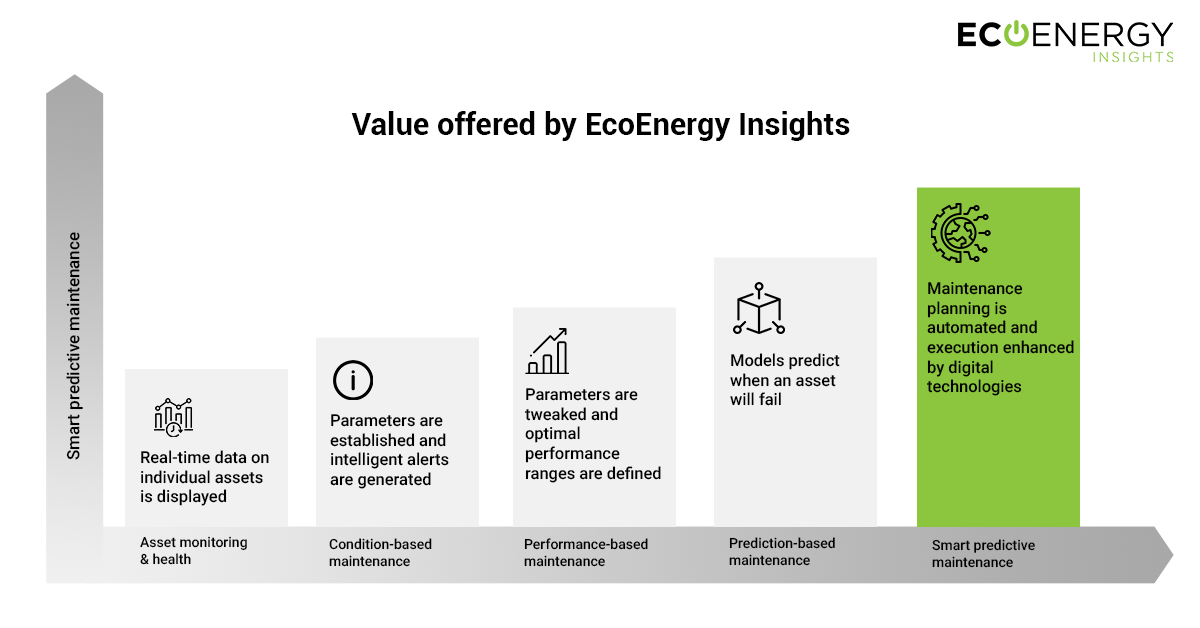
The CORTIX platform offers predictive insights and prescriptive recommendations on connected equipment. When the recommendations on the individual connected equipment are implemented, it helps facility managers bring visibility, agility and predictability to operations. BluEdge™ Command Centers offer 24x7 remote commissioning, monitoring and diagnostics as well as quick response support for on-site team and service technicians.
Solutions from EcoEnergy Insights leverage the CORTIX platform, combining artificial intelligence and IoT connectivity with the proactive actions of the BluEdge Command Center team, to digitally transform retail store operations.
April 2022
Author
Yudhajit Tornekar, Manager, Pre-Sales, EcoEnergy Insights
Yudhajit Tornekar manages pre-sales at EcoEnergy Insights. He is responsible for designing outcome-based services and packaging AI-enabled, IoT solutions for clients. He works on strategies for business expansion and supports sales and client engagement processes. Yudhajit has a passion for sustainable practices and driving efficient energy utilization in buildings.